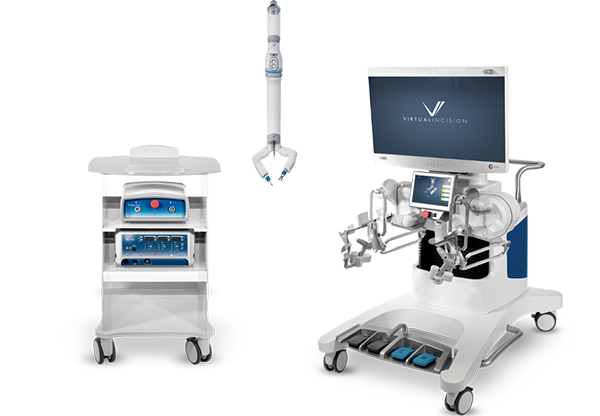
Virtual Incision Corp. today said it has raised $46 million in Series C funding. The Lincoln, Neb.-based company plans to use the financing to support regulatory and clinical programs leading to the commercialization of its MIRA surgical platform. MIRA stands for “miniaturized in vivo robotic assistant.”
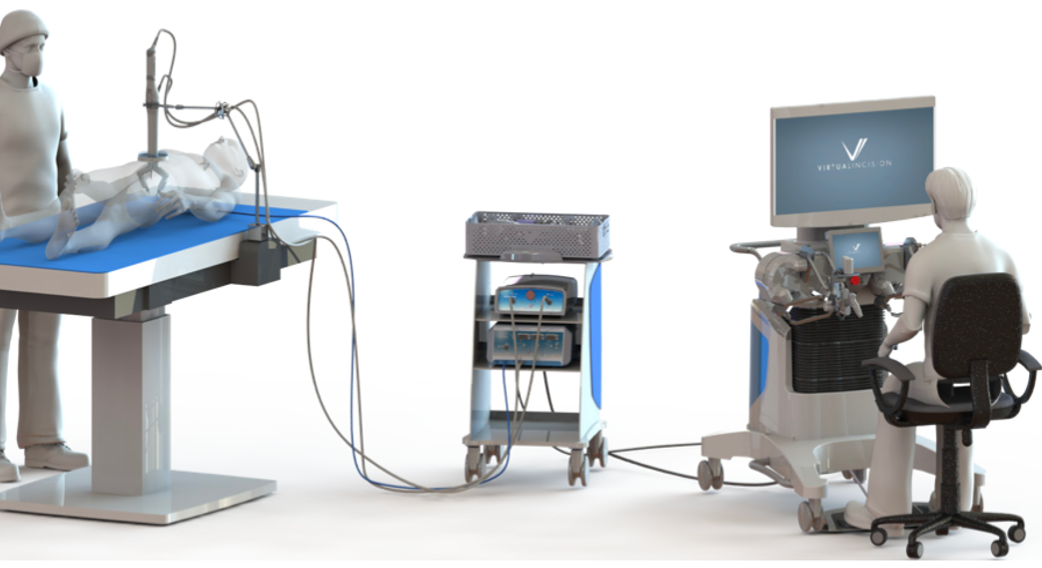
MIRA includes a small, self-contained surgical device that is inserted through a single midline umbilical incision in the patient’s abdomen. Virtual Incision said its technology is designed to support multi-quadrant abdominal surgeries using existing minimally invasive tools and techniques familiar to laparoscopic surgeons, and it does not require a dedicated operating room or specialized infrastructure.
The company added that it expects the device to be significantly less expensive than existing robotically-assisted surgical devices because of its smaller size. Weighing only 2 lb. (0.9 kg), the miniature single incision platform has full robotic capabilities and can easily be moved from room to room. Virtual Incision is focusing first on the use of MIRA for colon resection procedures, with follow-on robots for additional potential applications.
MIRA currently in IDE study
Virtual Incision recently announced the world’s first surgery using MIRA performed by Michael A. Jobst, M.D., at Bryan Medical Center in Lincoln, Neb. The robotically assisted right hemicolectomy procedure was performed as part of a clinical study of MIRA under an Investigational Device Exemption (IDE) from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
The study, which the company said is progressing well, is currently being conducted at a limited number of U.S. hospitals in support of the surgical system’s regulatory pathway to approval.
“The ability of MIRA to successfully perform colon resection—a challenging procedure in minimally invasive surgery that requires multi-quadrant anatomical access and significant robotic strength—demonstrates the huge potential of the platform,” said Shane Farritor, Ph.D., co-founder and chief technology officer of Virtual Incision. “This funding milestone represents a step forward in our goal to deliver a miniaturized solution for robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery, regardless of the site of care.”

Investors seek more portable robotic surgery
Endeavour Vision and Baird Capital led Virtual Incision's Series C round, with participation from returning investor Bluestem Capital and others.
“We are thrilled to have Endeavour Vision and Baird lead this round of financing at this important stage of our company’s growth, along with the continued strong support of our largest shareholder, Bluestem,” said John Murphy, Virtual Incision’s president and CEO. “Virtual Incision’s goal is to transform surgery by providing a practical and hassle-free platform that will enable efficient, effective, and affordable access to robotic-assisted technology.”
“While the demand for robotically assisted surgery continues to grow because of its clear benefits for patients, there are still challenges that hinder broader adoption, such as high cost, complex set-up, and required space and infrastructure,” said Robert Barmann, a partner at Endeavour Vision. “MIRA is intended to address the limitations associated with current mainframe robotic-assisted surgery systems through its small, mobile design that is streamlined for routine high-volume procedures.”
“MIRA is a space-saving solution designed to help hospitals and ambulatory surgery centers leverage their existing infrastructure to perform surgery efficiently while offering a low total cost of ownership,” said Amy Len Kobe, principal at Baird Capital. “Consistent with our venture team’s investment goals, the MIRA platform has the ability to improve care for patients, physicians, providers, and payors. And, best of all, it’s unlike any other surgical robotic platform available today.”

Virtual Incision to develop specialized systems
Funding from the round will also be used to support Virtual Incision’s research and development pipeline. Beyond its initial device design for colon resection, the company said it has begun developing a family of mini-robots optimized for operations such as hernia repair, gallbladder removal, hysterectomy, and sleeve gastrectomy, potentially enabling millions more surgical procedures each year.
Thanks to increasing regulatory approvals, the global market for surgical robots will exhibit a compound annual growth rate of 21.4%, growing from $1.4 billion in 2018 to $6.8 billion by 2026, predicted Fortune Business Insights. Kenneth Research was even more bullish, forecasting a cumulative market value of $91.5 billion by 2025.
With its foundational intellectual property, including more than 200 patents and applications, Virtual Incision claimeed that it is poised to lead the next wave of innovation in robotic-assisted surgery with its MIRA system.
Article topics
Email Sign Up