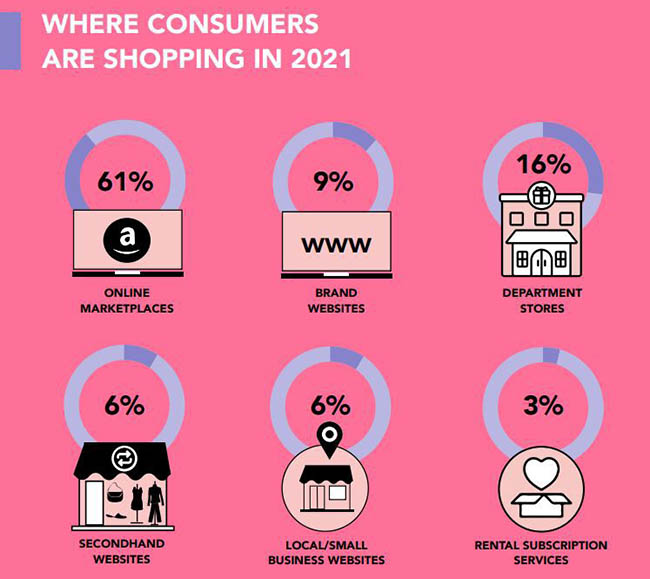
The pandemic has changed how consumers shop and make purchases. In spring 2020, nearly 70% of shoppers were reliant on online shopping. The infographic below outlines the top consumer shopping trends after COVID-19:
The National Retail Federation (NRF) estimates that holiday retail sales will increase between 8.5% and 10.5% this year. The NRF reports that online and non-store sales continue to experience significant gains, growing 11% to 15% in a market of about $218.3 billion to $226.2 billion. This growth is predicted to occur during the continued pandemic, supply chain constraints, inflation, and other market factors.
Retail distribution efficiencies are critical to the success of capturing and fulfilling consumers’ ecommerce holiday spend. Peak season is not limited to just Black Friday, the traditional single date of retail sales moving from the “red” to the “black” in revenues.
The holiday peak season now begins in October and extends to January. This includes Black Friday, Cyber Monday, and 12 days of Christmas promotions. Reverse logistics, the process of handling returns, is on-going and ramps up to high levels in January after the holidays as consumers return gifts and goods.
The retail market, among many others, requires optimized facilities, equipped to pick, pack, and ship with flawless execution. Multiple external forces will greatly impact the 2021 peak season, and facility optimization is a core requirement to the success of meeting consumer demand with accuracy and speed.
In this month's issue of Modern Materials Handling [a sibling publication to Robotics 24/7], Michael Levens, group editorial director, highlights how robotics continues to positively impact warehouses and distribution centers of small, midsize, and large facilities. Robots continue to dramatically help companies provide quality customer service and meet demands amid a challenging labor market.
RaaS makes it easier for SMBs to scale
Robotic automation is no longer limited to large corporations with the financial ability to heavily invest in capital equipment. Robots as a service (RaaS) is a viable option for businesses of all size and scale. The tight labor market is affecting businesses of all sizes, and robots can seamlessly fill the gaps, realigning workers to contribute in more meaningful ways.
Automation is providing nimble and promising solutions to warehouse and production problems from a labor shortages. Companies such as RIOS are leading the way with RaaS through a subscription-based program, which eliminates a CapEx purchase.
RIOS robotic workcells can help operations in three ways: production, quality control, and end-of-line packing. The company's systems offer viable opportunities for retail operations, fulfillment, and manufacturing facilities to revitalize their operations to meet customer demands with accuracy and speed, especially during peak season.
Article topics
Email Sign Up



















