Editors’ Picks




Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 39.04
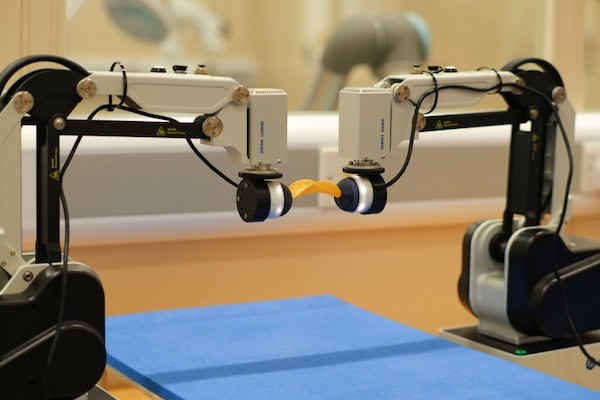
An innovative bimanual robot displays tactile sensitivity close to human-level dexterity using artificial intelligence to inform its actions. The new Bi-Touch system, designed by scientists at the University of Bristol and based at the Bristol Robotics Laboratory, allows robots to carry out manual tasks by sensing what to do from a digital helper. The findings, published in IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, show how an AI agent interprets its environment through tactile and proprioceptive feedback, and then control the robots' behaviors. The researchers said this enables precise sensing, gentle interaction, and effective object manipulation to accomplish robotic tasks. They added…
Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 31.16
…not only replicate our skin’s ability to precisely detect tactile information—like smoothness, hardness and pain—but also to mimic its signaling and decision-making capacity. Two new technologies point to a potential shift. These touch systems could well represent building blocks for designers to create products that interact with humans and their operating environment in an entirely new way. A New Tactile Sensor In the most recent development, researchers from Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology, ASML Korea Co., Dongguk University-Seoul, Sungkyunkwan University and the University of Oxford have developed a tactile sensor that aims to measure surface textures with high…

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 29.97
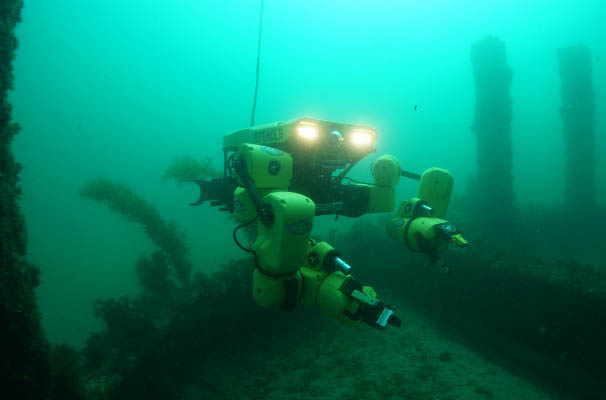
…explosive ordnance disposal, or EOD. STARFISH stands for “Strong Tactile mARitime hand for Feeling, Inspecting, Sensing and Handling.” Pittsburgh-based RE2, a wholly owned subsidiary of Sarcos Technology and Robotics Corp., said it has successfully assembled and lab-tested a complete gripper capable of grasping and holding a variety of objects. The end-of-arm tooling (EOAT) project is funded through the U.S. Navy's Office of Naval Research (ONR). “STARFISH uses advanced touch sensors and next-generation haptic feedback to provide robot operators with the last link in terms of robotic perception capabilities—the ability to ‘feel’ objects in the environment,” said Dr. Adam Brant, project…

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 25.46
…line of skin-like coverings, which include sensors to provide tactile awareness for humanoid robots and prosthetics. At less than 1 mm thick, RoboSkin fits robotic fingers, limbs, feet, heads, or torsos, to make robots “feel” better, said BeBop Sensors. RoboSkin’s advanced fabric-based sensor skin can be shaped to any surface, allowing quick tailoring to fit any robot, claimed the Berkeley, Calif.-based company. BeBob said its spatial resolution and sensitivity exceeds human abilities for collaborative applications. “I have been working with roboticists refining our RoboSkin for 10 years,” said Keith McMillen, founder and chief technology officer of BeBop Sensors. “We are…

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 20.34
…But now, a new frontier has opened – comprehending tactile sensations. Imagine a robotic finger gliding across a glass surface, identifying subtle imperfections, discerning temperature variations, and effortlessly distinguishing between metal and wood. In the dynamic landscape of today's technological frontiers, touch stands as a game-changer for robots and the industrial sectors they serve. Let’s delve into the latest advances in human-like touch and how they are propelling the world of robotics forward at an astonishing pace. Robotic hands gain human-like receptors The profound connection between the human experience and the nuances of touch is well known. Our tactile senses,…
Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 18.57
…said Hussein. “Companies have approached us after trying other tactile sensors on the market,” he said. “Other players such as SynTouch offer impressive capabilities, but their construction is complex and very rigid. Because their sensors are very expensive, they can do sensing only on the edge of the fingertip. To do sensing all over the hand, we can use biotactile sensors.” Touchlab goes for more modalities How close are Touchlab's thin eDermis sensors to human senses? “Lots of sensor companies look at the problem in a primitive way,” said Vasileios Mitrakos, senior electronic skin engineer at Touchlab. “Most sensors on…

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 18.24
…Samantha Johnson, named the system “TATUM,” which stands for “Tactile ASL Translational User Mechanism.” The genesis of the robot began when Johnson took a course in American Sign Language (ASL) in her second year at Northeastern. The course put her in touch with people at the Deaf-Blind Contact Center in Allston, Mass., where she was able to practice signing with the participants in the center. “When I was watching the interpreter sign, I asked, ‘How do you communicate without the interpreter?' and the answer was simply, 'We don’t,’” Johnson recalled. She set out to develop a robot interpreter. An inflatable…

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 17.82
…in Los Angeles, develops bio-inspired robot grippers: 1) a gecko-inspired gripper for handling large, flat objects and 2) a tactile gripper with compliant rubber tactile sensors (“skin”) to give robots a sense of touch. Its first grippers will be available this year.
Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 16.83
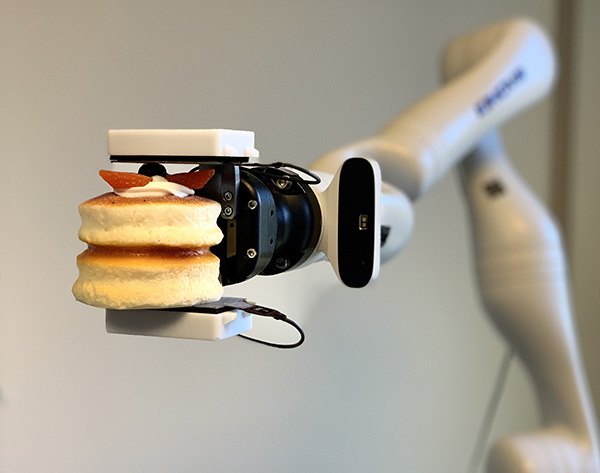
…avoid bruising. Scientists have recently made progress in developing tactile sensors to enable robots to approach or surpass human-level motor skills and meet growing industry needs. Researchers at Mitsubishi Electric Research Laboratories (MERL) have been working with the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology on a prototype collaborative robot with tactile sensor technology. The ability to grasp, lift, and place food items without damaging them also has implications for manufacturing, healthcare and pharmaceuticals, and ultimately home robots, according to MERL. Robotics 24/7 recently spoke with Daniel Nikovski, manager of the data analytics group; Allan…

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 16.01
…is customized according to different customer needs. Compared with G1, G1 EDU supports Dex3-1 force-controlled dexterous hand installation, optional tactile sensor arrays, greater knee joint torque and arm load and optional NVIDIA Jetson Orin high computing power module to support secondary development.

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 15.45
…has 12 active degrees of freedom. It boasts built-in tactile sensors, a simple transmission structure, powerful motor joints and other in-house technologies. They not only bolster motion control precision, but also contribute to smooth and reliable operation. Embedded into each fingertip of the XHand are highly sensitive array sensors that collect and generate information including the size, shape, texture, softness and force feedback of the object being grasped. The dexterous hand generates a maximum force of 80 neutrons and exceeds human capabilities in object grasping. With a high payload, it is designed to hold heavy items like a 5kg bottle…

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 15.21
…its RoboSkin product line, which is designed to provide tactile awareness for humanoid robots and prosthetics. BeBop said millions of its fabric sensors are already in daily use in research, corporate, and military facilities worldwide. “We started shipping RoboSkin to evaluation customers two years ago,” recalled Keith McMillen, founder and chief technology officer of BeBop Sensors. “We got good feedback and decided to give it better spatial resolution than human skin and significantly better force recognition.” How to identify superhuman sensing What is “better-than-human spatial resolution,” and how can that help robots? “Physiologists have experimented and touched a person with…



