The use of industrial robots in factories around the world has continued to accelerate, said the International Federation of Robotics today. The average robot density is now 126 robots per 10,000 employees in manufacturing – nearly double the number of 66 units in 2015, according to the
“2021 World Robot Report.”
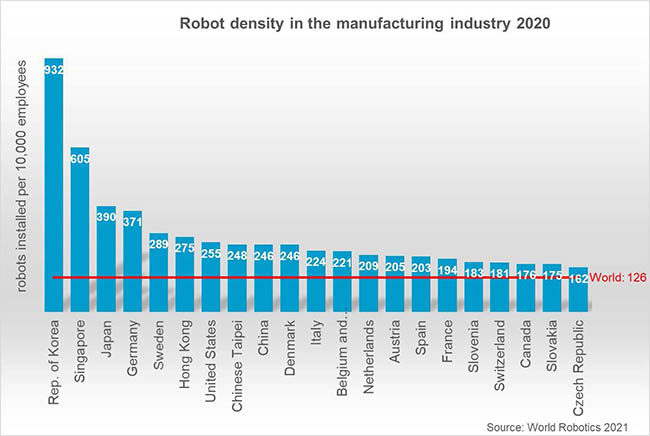
By regions, the average robot density in Asia/Australia is 134 units, in Europe 123 units, and in the Americas 111 units. The top five most automated countries in the world are South Korea, Singapore, Japan, Germany, and Sweden, according to the International Federation of Robotics (IFR).
“Robot density is the barometer to track the degree of automation adoption in the manufacturing industry around the world,” stated Milton Guerry, president of the IFR.
China leads Asian robotics usage
The development of robot density in China is the most dynamic worldwide, said the IFR. Due to the significant growth of robot installations, the density rose from 49 units in 2015 to 246 units per 10,000 workers in 2020. Today, China’s robot density ranks ninth globally, compared with 25th just five years ago.
Asia is also the home of the country with the world´s highest robot density. The Republic of Korea has held this position since 2010. The country’s robot density is seven times the global average, at 932 units per 10,000 workers.
Robot density in South Korea had been increasing by 10% on average each year since 2015. With its globally recognized electronics industry and a distinct automotive industry, the Korean economy is based on the two largest areas for industrial automation, said the IFR.
Singapore took second place, with a rate of 605 robots per 10,000 employees in 2020. Singapore’s robot density had been growing by 27% on average each year since 2015.
Japan ranked third in the world in 2020, with 390 robots installed per 10,000 employees in the manufacturing industry. Japan is the world´s predominant industrial robot manufacturer. The production capacity of Japanese suppliers reached 174,000 units in 2020. Today, Japan´s manufacturers deliver 45% of the global robot supply.
North America starts to automate for sustainability
Robot density in the U.S. rose from 176 units in 2015 to 255 units in 2020. It ranks seventh in the world – ahead of Chinese Taipei (248 units) and China (246 units), said the IFR. The modernization of domestic production facilities has boosted robot sales in the U.S., it said.
The use of industrial robots in the cost-efficient production of solar panels and in the continued transition towards electric vehicles is helping manufacturers achieve decarbonization targets.
Several car manufacturers have announced investments to further equip their factories for new electric drive car models or to increase capacity for battery production. These major projects will create demand for industrial robots in the next few years.
European growth is slow, as Germany and the U.K. recover
Europe´s most automated country is Germany, which ranked fourth worldwide with 371 units. The annual supply had a share of 33% of total robot sales in Europe for 2020, and 38% of Europe’s operational stock is in Germany. The German robotics industry is recovering, mainly driven by strong overseas business rather than by the domestic or European market, said the IFR.
Robot demand in Germany is expected to grow slowly, mainly supported by demand for low-cost robots in the general industries and outside traditional manufacturing, reported the organization.
France has a robot density of 194 units, ranking 16th in the world, which is well above the global average of 126 robots and similar to other EU countries like Spain (203 units), Austria (205 units), or the Netherlands (209 units).
EU members like Sweden (289 units), Denmark (246 units), or Italy (224 units), have a significantly higher degree of automation in manufacturing.
As the only G7 country – the U.K. has a robot density below the world average of 126 units with 101 units, ranking 24th. Five years ago, the U.K.'s robot density was 71 units. The exodus of foreign labor after Brexit increased the demand for robots in 2020.
This situation is expected to continue in near future, and the modernization of British industry will also be boosted by major tax incentives, reported the IFR. With the “super-deduction” from April 2021 until March 2023, U.K. companies can claim 130% of capital allowances as a tax relief for plant and machinery investments.
Article topics
Email Sign Up

















