The International Federation of Robotics has released a new report noting that the automotive industry has the largest number of robots working in factories around the world. Operational stock hit a new record of about a million units in 2021, according to IFR.
“The automotive industry effectively invented automated manufacturing,” said Marina Bill, president of the IFR. “Today, robots are playing a vital role in enabling this industry’s transition from combustion engines to electric power. Robotic automation helps car manufacturers manage the wholesale changes to long-established manufacturing methods and technologies.”
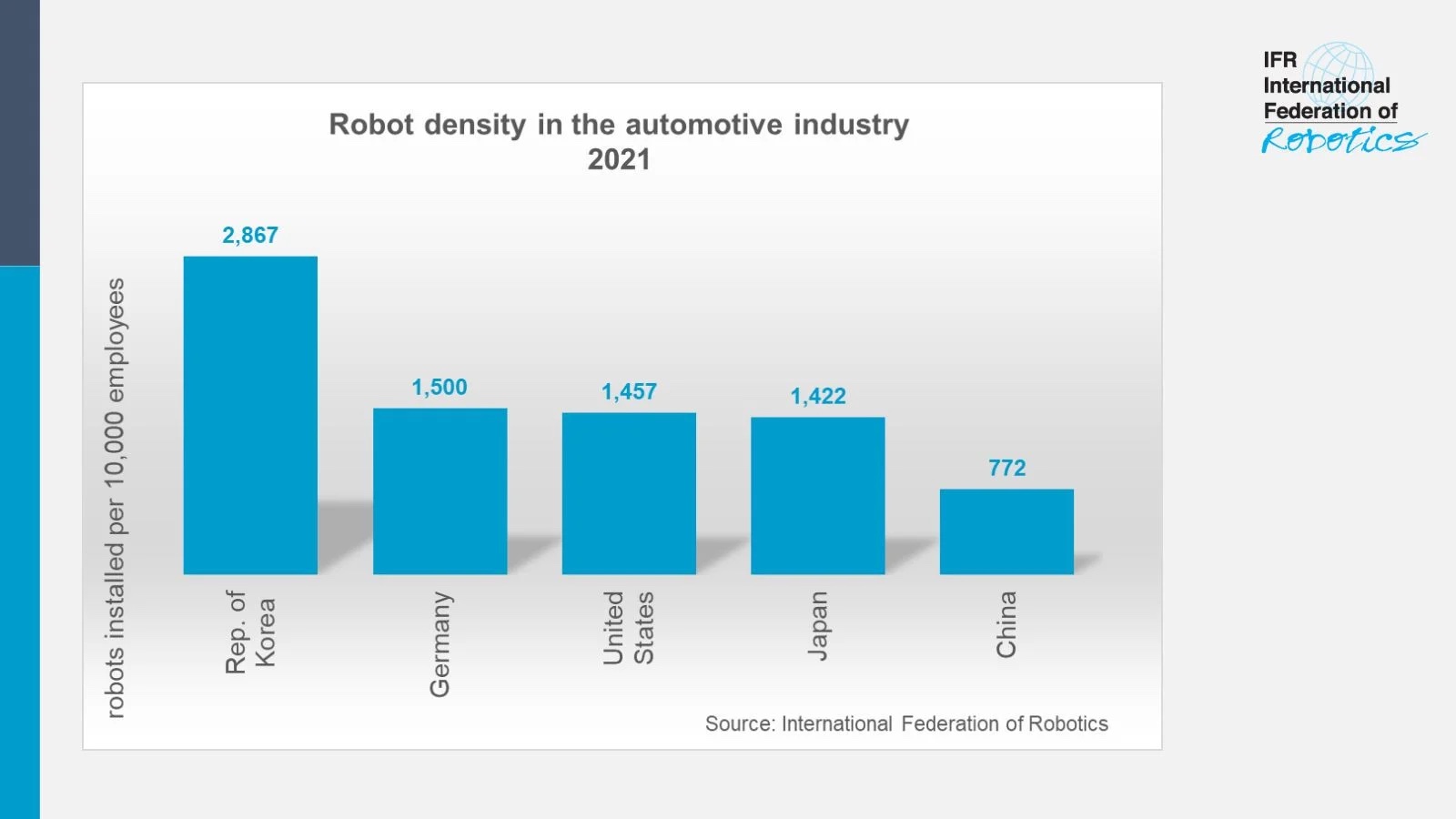
China’s robot density is growing fast
In the Republic of Korea, 2,867 industrial robots per 10,000 employees were in operation in 2021. Germany ranks in second place with 1,500 units followed by the United States counting 1,457 units and Japan with 1,422 units per 10,000 workers.
The world´s biggest car manufacturer, China, has a robot density of 772 units, but is catching up fast: Within a year, new robot installations in the Chinese automotive industry almost doubled to 61,598 units in 2021- accounting for 52% of the total 119,405 units installed in factories around the world.
IFR highlighted a number of governmental developments that are forcing the car industry to invest in electric vehicles.
Electric vehicles drive automation
The European Union has announced plans to end the sale of air-polluting vehicles by 2035. The US government aims to reach a voluntary goal of 50% market share for electric vehicle sales by 2030 and all new vehicles sold in China must be powered by “new energy” by 2035.
Half of them must be electric, fuel cell, or plug-in hybrid – the remaining 50%, hybrid vehicles.
Most automotive manufacturers who have already invested in traditional “caged” industrial robots for basic assembling are now also investing in collaborative applications for final assembly and finishing tasks.
Tier-two automotive parts suppliers, many of which are SMEs, are slower to automate fully. Yet, as robots become smaller, more adaptable, easier to program, and less capital-intensive this is expected to change, IFR noted.
Article topics
Email Sign Up