Editors’ Picks





Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 14.34
…OpenAI and MIT’s Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL). While the former is better known today for ChatGPT, in 2018, it made headlines by training a human-like robot hand to manipulate physical objects with unprecedented dexterity by using a reinforcement learning algorithm and code. CSAIL also relied on advances in deep learning to reorient a robotic hand to handle over 2,000 objects. As the pace of AI innovation continues to accelerate, we’re not far from seeing deep learning models for robotic dexterity deployed in real-world assembly lines. Giving robots awareness of their hands and feet The final sense of…
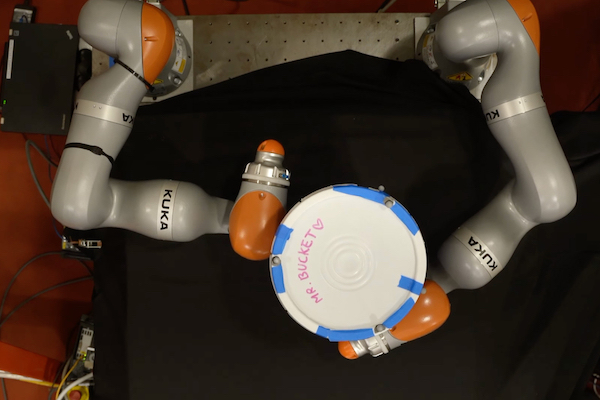

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 9.63
…member of MIT's Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) In these figures, a simulated robot performs three contact-rich manipulation tasks: in-hand manipulation of a ball, picking up a plate, and manipulating a pen into a specific orientation. Source: MIT, courtesy of the researchers Reinforcement learning versus smoothing Reinforcement learning is a machine learning technique where an agent, like a robot, learns to complete a task through trial and error with a reward for getting closer to a goal. The researchers said this type of learning takes a black-box approach because the system must learn everything about the world through…

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 25.46
…Researchers at MIT’s Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) are using machine learning to cut down on the typical iterative process of task planning that considers all possible actions. PIGINet eliminates task plans that can’t satisfy collision-free requirements, and it reduces planning time by 50% to 80% when trained on only 300 to 500 problems. Typically, robots attempt various task plans and iteratively refine their moves until they find a feasible solution, which can be inefficient and time-consuming, especially when there are movable and articulated obstacles. Maybe after cooking, for example, you want to put all the sauces in…
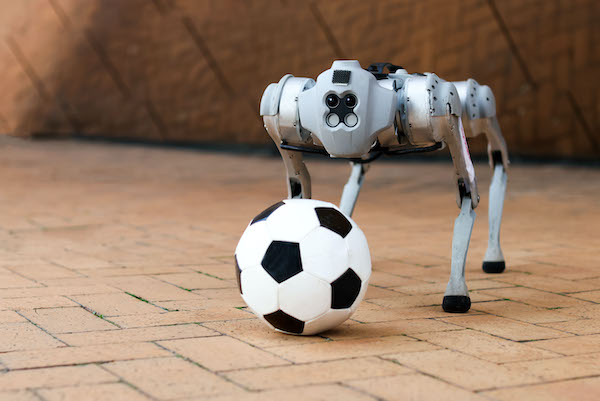

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 17.71
…part of its Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL), have developed a legged robot that can dribble a soccer ball under the same conditions as humans. The robot used a mixture of onboard sensing and computing to traverse different natural terrains such as sand, gravel, mud, and snow. It could also adapt to their varied impact on the ball’s motion. Like any committed athlete, “DribbleBot” could get up and recover the ball after falling. MIT team turns to simulation to train robot Programming robots to play soccer has been an active research area for some time. However, MIT's team…

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 13.61
…Daniela Rus, Director, Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) and MacArthur Fellow, and Saman Amarasinghe. LG Technology Ventures, established in 2018 in Silicon Valley, is the venture capital investment arm of the Korea based LG Group. Its team consists of experienced investors, entrepreneurs, technologists and industry domain experts. LG Technology Ventures manages over $500 million of fund assets and invests in early-stage start-ups in artificial intelligence, mobility, electrification, advanced materials, climate technologies, life-sciences, next generation display, XR, Web3, mobile and 5G. “Venti is solving real-world problems for large customers in huge markets with technology that has proven safe, mature…

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 14.34
…Technology, its Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (MIT CSAIL) touted its alliances program. CSAIL Alliances offers companies opportunities to engage with its students and researchers, and its membership includes more than 1,200 people. The institute also showed off one of its four-legged robots. Earlier this year, a version of the robot beat a world record for the being the fastest legged robot. Onshape Inc. showed how its computer-aided design (CAD) software enables developers to design parts for robots and other systems. A robot designed with Onshape that shot table-tennis balls into a net was popular with small children. In…

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 18.31
…director of the Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) at MIT. “The Robotics Medal means more than its generous cash prize and resources at MassRobotics,” Rus added. “It reflects the powerful contributions women have made, are making, and will make to this important, vibrant and growing industry.” Winner will have access to MassRobotics' network The Robotics Medal recipient will be named a MassRobotics Fellow and gain access to manufacturing and robotics expertise through the MassRobotics network, along with access to robotics labs and office space at MassRobotics in Boston. At the facility, the winner will have access to prototyping…
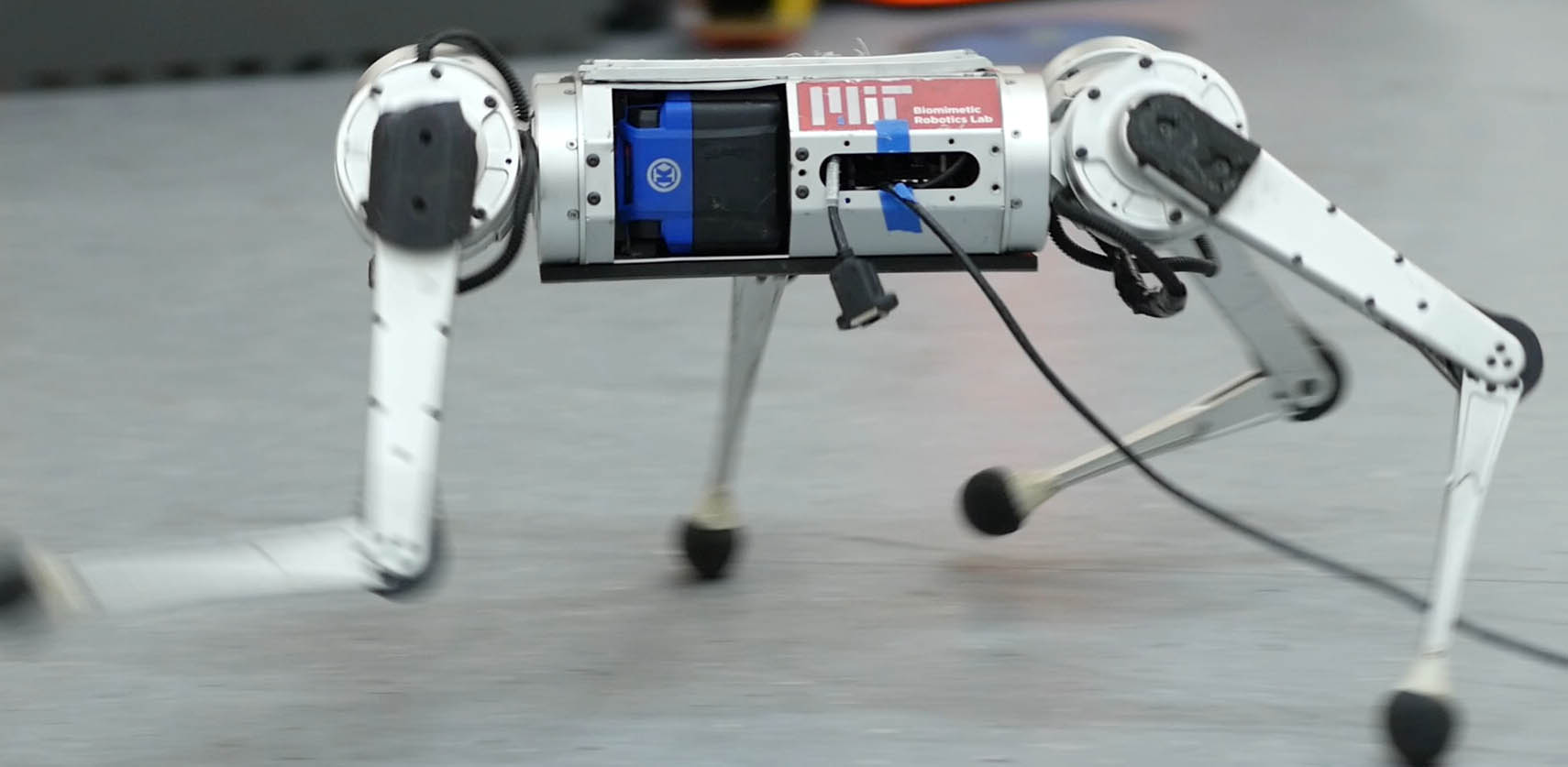
Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 12.78
…student at MIT Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL), and Ge Yang, a postdoctoral fellow at the Institute of AI and Fundamental Interactions (IAIFI), about just how fast the quadruped robot can run. Q: We’ve seen videos of robots running before—why is running harder than walking? Achieving fast running requires pushing the hardware to its limits, for example by operating near the maximum torque output of motors. In such conditions, the robot dynamics are hard to analytically model. The robot needs to respond quickly to changes in the environment, such as the moment it encounters ice while running on…
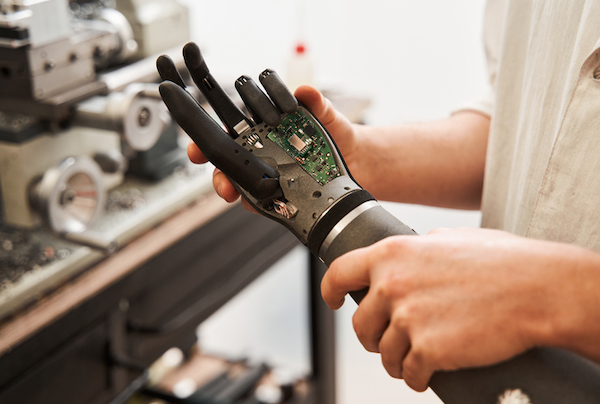

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 15.05
…Institute of Technology's Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) has developed an algorithm for efficient motion control. It enables a robot to move while ensuring the physical safety of its human user. The MIT scientists used it to program a robot to help a person with limited mobility to put on a jacket. The laboratory began by modeling how humans move, react, and respond. With that data, the scientists built algorithms for orchestrating human interactions with robots while incorporating trial and error. To assist a human, there are numerous models to follow. Training a robot in only one scenario…

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 10.99
…Group of MIT's Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) and lead author of the paper. This is particularly true in the manufacturing and health care industries. “Whether or not we try to help people build conceptual models of robots, they will build them anyway,” she said. “And those conceptual models could be wrong. This can put people in serious danger. It is important that we use everything we can to give that person the best mental model they can build.” Theoretical approaches should be deliberate While many research papers incorporated partial elements of one theory, this was most likely…
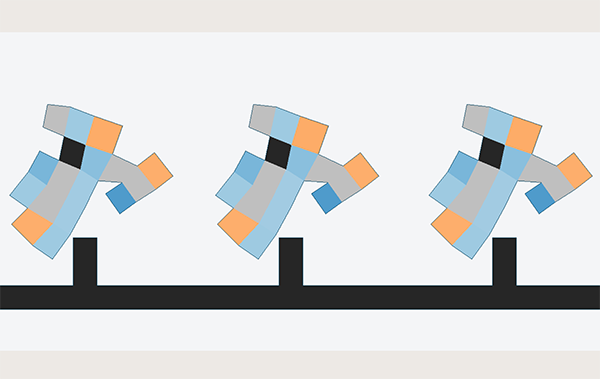
Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 28.39
…Scientists at MIT’s Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL), aimed to fill the gap by designing “Evolution Gym,” a large-scale testing system for co-optimizing the design and control of soft robots, taking inspiration from nature and evolutionary processes. Simulations soft robots learn on their own The robots in the simulator look a little bit like squishy, moveable Tetris pieces made up of soft, rigid, and actuator “cells” on a grid, put to the tasks of walking, climbing, manipulating objects, shape-shifting, and navigating dense terrain. To test the robot’s aptitude, the team developed their own co-design algorithms by combining standard…
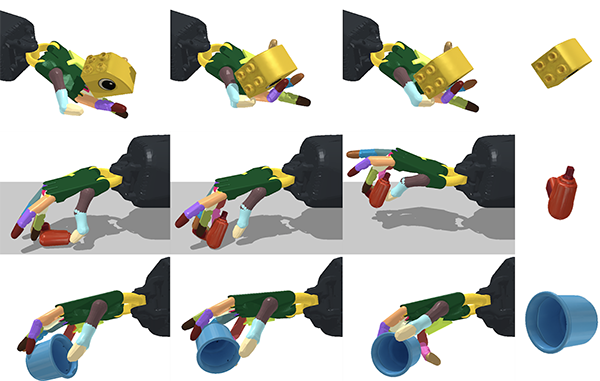
Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 31.20
…the MIT’s Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (MIT CSAIL) created a framework that’s more scaled up. They built system that can reorient over 2,000 different objects, with the robotic hand facing both upwards and downwards. This ability to manipulate anything from a cup to a tuna can or a Cheez-It box could help the hand quickly pick and place objects in specific ways and locations—and even generalize to unseen objects. Greater dexterity has industrial implications Deft “handiwork”—which is usually limited by single tasks and upright positions—could be an asset in speeding up logistics and manufacturing, said MIT CSAIL. Such…



