Editors’ Picks





Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 35.03
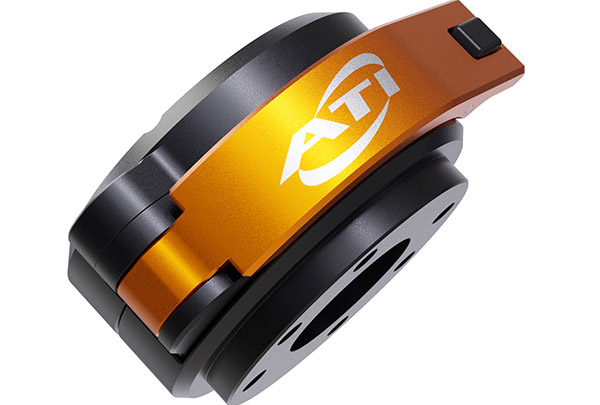
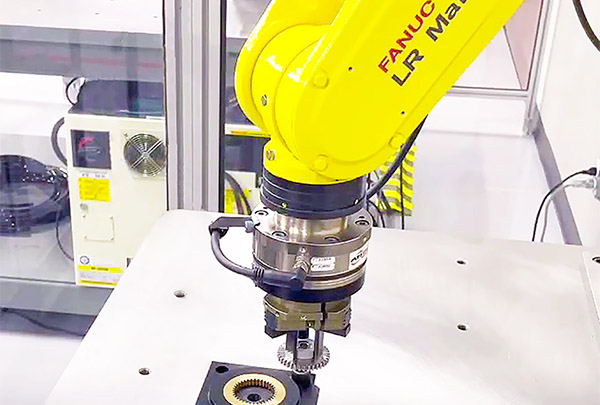
…its force/torque sensors are compatible with FANUC's robots and Force Control Software. Organizations including including NASA, Ford, Honda, and Johns Hopkins University use ATI products, said the unit of Novanta Inc. Want to learn more about cobot arms? This article was featured in the April 2024 Robotics 24/7 Special Focus Issue titled “Collaborating with robot arms, platforms.”

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 32.11
…different tasks. Leading organizations including NASA, Ford, Honda, and Johns Hopkins University use the company's products. ATI F/T Sensors enable precise tasks ATI Industrial Automation said the integration of its Multi-Axis Force/Torque Sensors with FANUC's hardware and software will enable users to achieve greater levels of accuracy, flexibility, and responsiveness. Integrators and manufacturers will be able to take advantage of the enhanced sensing capabilities, it said. ATI and FANUC have integrated F/T sensors and robot arms. Source: ATI Industrial Automation ATI said its F/T Sensors can “provide accurate measurements of forces and torques in multiple axes, enabling robots to have…

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 39.26
…Ohio-based startup is a spinout of robotics research from Johns Hopkins University. Kel Guerin was a Ph.D. candidate there leading this research when he partnered with Benjamin Gibbs, who was at Johns Hopkins Technology Ventures. They obtained funding and lanched READY Robotics, now led by Gibbs as CEO. “There was this 'a-ha' moment where we figured out that we could take these types of visual languages that are very easy to understand and use them for robotics,” stated Guerin, who is now chief innovation officer at the company. ForgeOS supports third-party apps READY Robotics said its “no-code” operating system is…
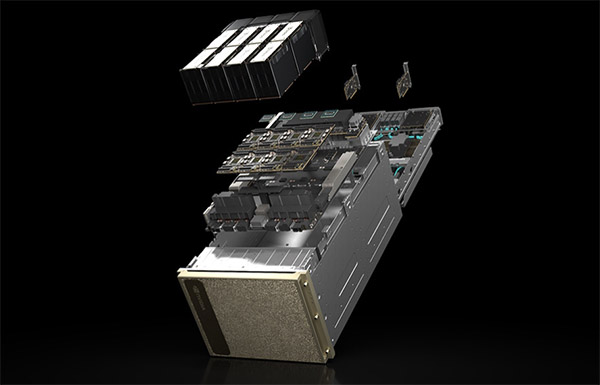
Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 29.01
…of DGX H100 systems. Lighting up around the globe Universities from Singapore to Sweden are plugging in DGX H100 systems for research across a range of fields. A DGX H100 will train large language models for Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory. The KTH Royal Institute of Sweden will use one to expand its supercomputing capabilities. Among other use cases, Japan’s CyberAgent, an internet services company, is creating smart digital ads and celebrity avatars. Telconet, a leading telecommunications provider in Ecuador, is building intelligent video analytics for safe cities and language services to support customers across Spanish dialects. An engine…

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 55.29
…surgeons relief from tremors and fatigue and increasing precision. Johns Hopkins research goes to market Founded in 2016, Galen Robotics is commercializing surgical robotics research at Johns Hopkins University in combination with big data analytics from Silicon Valley. The company moved from San Jose, Calif., to Baltimore shortly before the COVID-19 pandemic. “Dr. Russell Taylor, whose IP [intellectual property] is at the core of a lot of surgical robotics, runs the lab at Johns Hopkins,” said Dave Saunders, co-founder and chief technology officer of Galen Robotics. “Doctors asked for robots for complex, soft-tissue procedures, which gave rise to a Ph.D.…

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 25.47
…robot used to perform soft tissue laparoscopic surgery At John Hopkins University, researchers have deployed a smart tissue autonomous robot (STAR) that performed a laparoscopic surgery on a pig. The event is a precursor to what's possible for humans: soft tissue surgery performed by a robot. Surgeons require years of practice to become skilled at performing this type of surgery. It involves connecting two ends of an intestine. It is a challenging procedure, perhaps one of the most challenging in gastrointestinal surgery. Normally, a surgeon sutures the intestinal tissues with precision, being careful to do so without causing infection. There's…

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 71.64
…automated surgery is progressing. A team of researchers at Johns Hopkins University yesterday announced that the Smart Tissue Autonomous Robot, or STAR, has performed laparoscopic surgery on the soft tissue of a pig without human guidance. The researchers described their work in Science Robotics. “Our findings show that we can automate one of the most intricate and delicate tasks in surgery: the reconnection of two ends of an intestine,” said Axel Krieger, an assistant professor of mechanical engineering at Johns Hopkins' Whiting School of Engineering and senior author. “The STAR performed the procedure in four animals and it produced significantly…

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 28.83
…Kravitz has taught as an adjunct professor at The Johns Hopkins University and has significant experience exploiting emerging tools and techniques to rapidly transform new ideas into manufactured products. He is an experienced executive and entrepreneur serving as CEO, chief operating officer, president, and vice president of numerous Fortune 500 companies. Kravitz has also served on several corporate boards. He holds a master’s degree in electrical engineering from Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute. In his new role, Kravitz will drive the ARM Institute’s innovation activities, to evolve and grow the organization. He will work to advance its mission of increasing U.S. global…

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 26.86
…It and its portfolio companies work with partners including Johns Hopkins University, Minderoo Foundation, the National Science Foundation, the Nature Conservancy, the Wildlife Conservation Society, and WorldFish. San Francisco-based Good Machine's projects include ReefGen, an underwater, dexterous, planting robot intended to revive marine ecosystems and coral tourism around the world. Other projects include Fresure, a shipping container that uses solar panels to keep perishable foods cold during handling and storage to reduce post-harvest losses and relieve food insecurity. Good Machine's wildfire detection project aims to use stratospheric balloons for early detection of wildfires to help reduce catastrophic damage. Plus and…
Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 22.80
…with Raytheon Technologies, the Penn State Applied Research Lab, Johns Hopkins University and Identify3D, the goal is to optimize a component relative to an Army modernization product to maximize cooling and improve overall system performance. Using additive manufacturing (AM) to address this need is a novel approach to the project that covers the entire part lifecycle including determining performance requirements, topologically optimizing the design, manufacturing the part with attention to process monitoring for quality control, component performance validation, and data security. “The novel integration and concurrent design of structures, materials, and processes to create topologically optimized heat exchangers will enable…



