Last month, READY Robotics introduced Forge Edge—an industry-first API compatible with hundreds of different models of robots and cobots from ABB, Epson, Fanuc, Kawasaki, Staubli, Yaskawa, Universal Robot, and more.
Meanwhile, OpenAI's ChatGPT has blazed a trail for Large Language Models (LLMs), setting the AI world on fire. In Microsoft's paper “ChatGPT for Robotics: Design Principles and Model Abilities,” a key challenge in applying AI innovation to robotics is observed:
“Robotics is a diverse field where several platforms, scenarios, and tools exist. There exists an extensive variety of libraries and APIs….”
The paper proposed a higher-level function library and prompt engineering tools to control robots with natural language. LLMs have huge potential in robotics, a topic that READY Robotics co-founder and CIO, Kel Guerin, will delve into deeper in a future article.
The focus of this article is applying such innovations—and solving the gnarly problem of the myriad of robot languages and drivers proprietary to specific robot vendors. As an example, we show how we built a vendor-agnostic robot plugin for ChatGPT-4.
Accelerating development
As anyone who has developed software for industrial robots is painfully aware, the software standardization that allowed the PC and mobile markets to flourish has yet to take hold. This is what READY Robotics has solved.
ForgeOS is a platform based on proven drivers that abstracts fragmentation, enabling the deployment of software to trusted hardware in a secure, scalable, vendor-agnostic way. Forge Edge provides a REST API to ForgeOS:
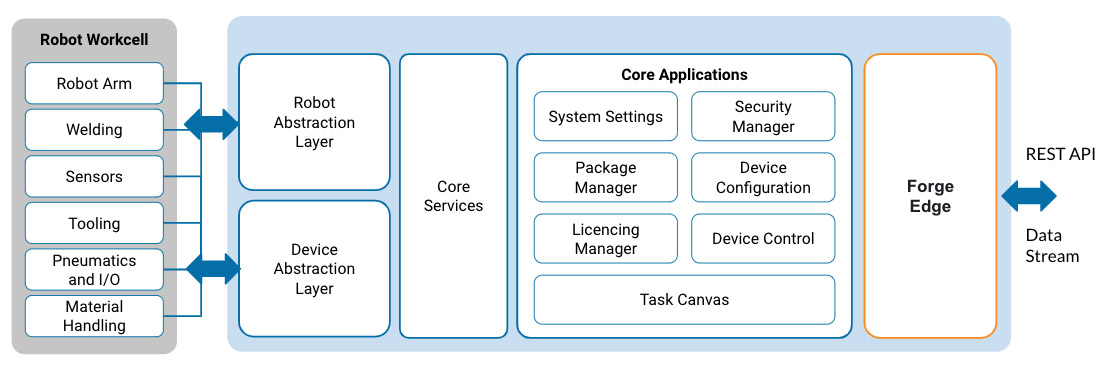
The implications for the broader industrial space are transformative. READY Robotics accelerates the integration of software platforms, from ERP to ChatGPT, to solve real-world industrial automation problems.
Building a Forge Edge plugin for ChatGPT
We built a Forge Edge plugin for ChatGPT that can communicate with hundreds of models of robots and cobots via ForgeOS. ChatGPT plugins are extensions that allow ChatGPT-4 to interact with the outside world —to scrape websites, access online services, and in our demo, communicate with live robots.
To build a ChatGPT plugin, you first need to join OpenAI’s waitlist to gain developer access. Once you have access (which we finally have!), you can follow the Getting Started guide on the OpenAI website. The three main components we provided ChatGPT in order to register our plugin were:
A short plugin manifest served from /.well-known/ai-plugin.json
An OpenAPI (Swagger) json document for the Forge Edge API
A proxy that relays API calls from ChatGPT to Forge Edge on an IPC.
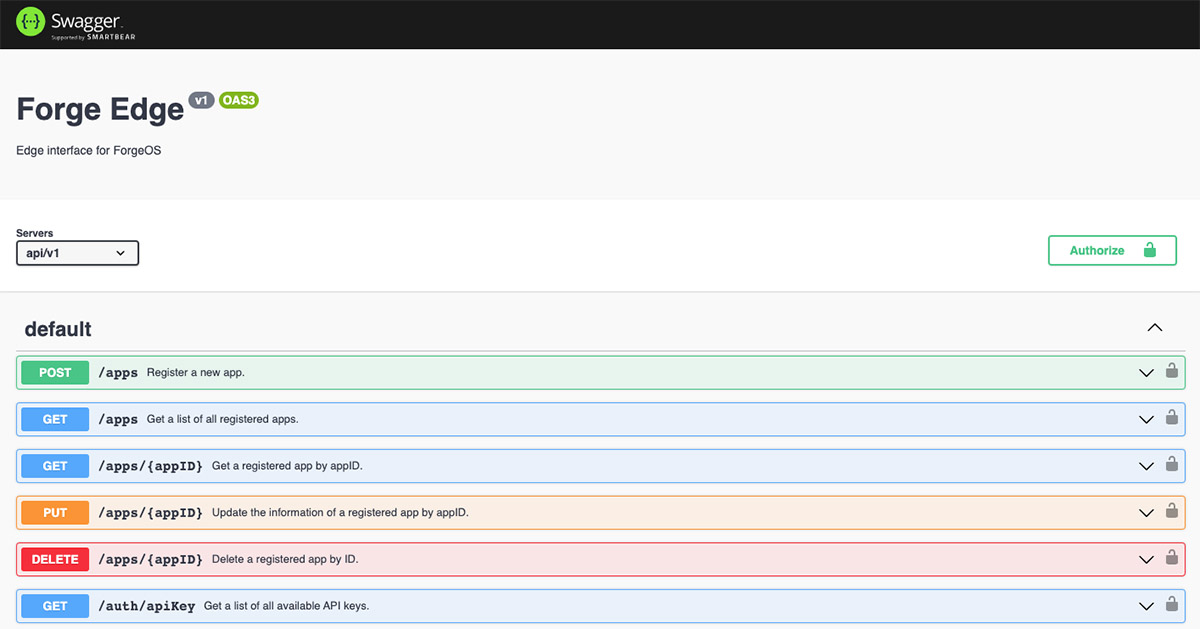
It's amazing that ChatGPT learns the API by just reading the OpenAPI document! Since we already serve an OpenAPI document directly from Forge Edge, ChatGPT plugins can immediately support it—although we did choose a manageable subset of API endpoints for this demo.
Forge Edge is served from an Industrial PC, not the cloud, and for the final piece we used a proxy server which OpenAI also provides code for a Python example. (Inferencing at the edge is a topic we'll explore at a later date, given the latency, privacy, and reliability advantages.)
Installing the plugin
With our proxy running on localhost:3333, installing the plugin was done directly through OpenAI's chat.openai.com web interface:
Through the plugin, ChatGPT-4 learns new skills provided by the READY Robotics Forge Edge API, allowing it to immediately handle prompts by querying the live state of our robot, listing tasks, and even starting or stopping a task remotely, as you can see in our video:
Safety is of paramount importance to us at READY Robotics. Our demonstration robot was in an enclosure with a safety door and installed according to safety and security best practices, with remote control enabled and acknowledged by the robot operator.
It is not recommend to connect LLMs directly to robots without appropriate safeguards in place.
Behind the scenes
When ChatGPT gets our text prompts, it checks against the Forge Edge API to see if there are any functions that can help it respond:

In this case, it ran the /tasks command to get a list of available tasks on our demo ForgeOS instance connected to a Yaskawa GP8 robot:
These are just simple prompts, and there is plenty of room for optimization and development beyond this approach, but it was great to see working!
Conclusion
Building this ChatGPT integration only took a day or so, as Forge Edge is a working, well-documented, standard interface to the ForgeOS platform that already supports hundreds of robots. This practical demonstration underscores how Forge Edge can simplify the integration of industrial robots with any software.
The future of software-defined automation beckons. With READY Robotics, you can build industrial automation apps that truly scale.
Sign up for the private beta of Forge Edge, and get updates on this and future integrations.

About the author
Dominic Pajak is vice president of developers at READY Robotics. He consults with major manufacturing enterprises on digital transformation and automation, applying advanced AI, the Internet of Things (IoT), and augmented/virtual reality (XR) technology to industry-proven robotics. This article is reposted with permission.
Article topics
Email Sign Up
















