Today Samsung Electronics has proven to be one of the most successful global brands to follow.
In supply chain management context, they has demonstrated operational excellence that leads them to supply chain hall of fame. In this article, we will explain to you how they do it.
Background
“Samsung” in Korean language means “3 stars” or “tri stars”. At first, they had a strong root in trading business. Later, they took the diversification strategy and entered electronic industry by producing black-and-white TV set.
Anyway, the rise of Samsung started when Lee Kun-Hee succeeded his father as a second chairman of the company.
During 1990s, he noticed that many Japanese companies who were the leaders in analog technology hesitated to adopt digital technology. Then he gradually created transformations that later change the face of the entire industry.
How do they build superb supply chain management capabilities? We investigate further and find 3 related articles as below;
The Paradox of Samsung’s Rise on Harvard Busienss Review
by Tarun Khanna, Jaeyong Song, and Kyungmook Lee
Like today’s emerging giants, Samsung faced a paradox: The tightly integrated business system that worked in its home market could not secure its future in global markets. So into an organization focused on continuous process improvement, Samsung introduced a focus on innovation.
Supply chain management six sigma: a management innovation methodology at the Samsung Group on Supply Chain Management: The International Journal
by Emerald Management First
Samsung’s effort and investment has turned out to be fruitful. Their SCM six sigma program has produced highly qualified and talented SCM specialists, who are currently training the methodology to other members in their organizations and leading SCM projects.
An Analysis of Sources of Risk in the Consumer Electronics Industry on Journal of the Operational Research Society
by ManMohan S. Sodhi, Cass Business School and Seongha Lee, Samsung
The consumer electronics industry is a $ 240 billion global industry with a small number of highly competitive global players. We describe many of the risks associated with any global supply chain in this industry.
Then we analyze these case studies and extract information related to supply chain management which is summarized as below;
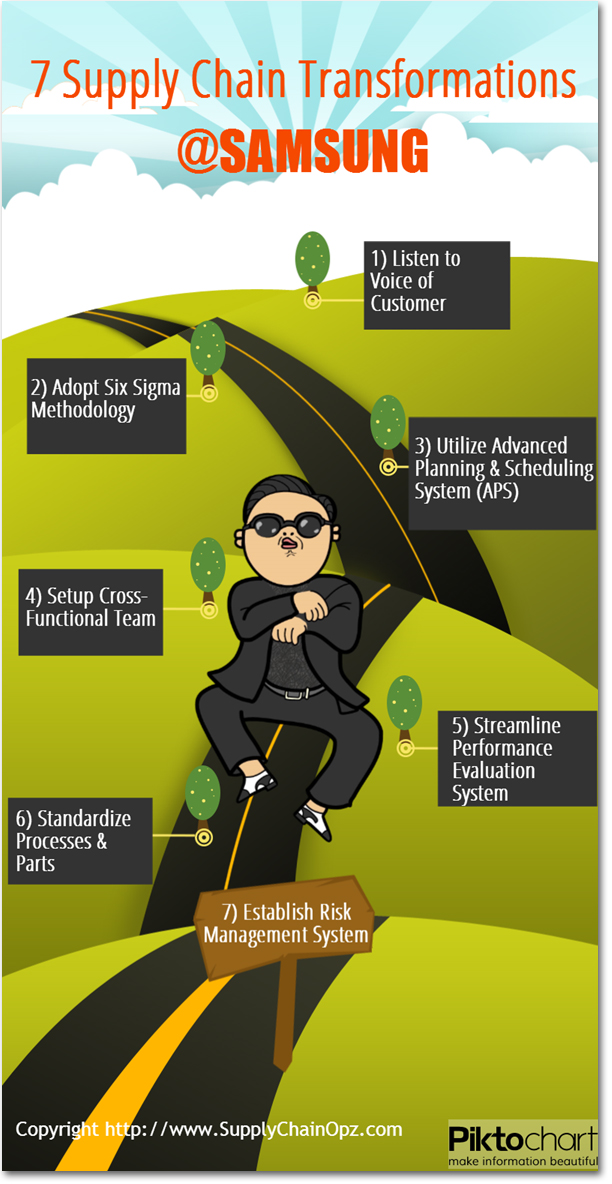
7 Supply Chain Transformations
- Listen to Voice of Customer: At the macro level, Samsung tries to understand behavior of consumers in particular country by sending staffs to attend MBA programs at local universities. These “Country Specialists” also establish connection with business leaders and potential business partners. At micro level, they gather customer preferences and incorporate them into product design through a method called “Quality Function Deployment”.
- Adopt Six Sigma Methodology: Based on “quality movement” in electronics industry, Samsung believes they can improve internal operations drastically using Six Sigma. Then they study various Six Sigma approaches from GE, Dupont and Honeywell. Later, they create a methodology based on GE approach called “DMAEV” (define, measure, analyze, enable and verify).
- Utilize APS system: Since electronics market changes quickly, they need to be able to create flexible production plan. So they implement APS system which brings remarkable success.
- Setup Cross Functional Team: In order to bring internal departments closer, they use the system called “Voice of Business”. What they do is to gather internal requirements and establish action plans based on collective decision.
- Streamline Performance Evaluation System: The classic problem of many organizations Asia is seniority based performance evaluation system. Samsung thinks they won’t be able to attract the best and the brightest to help them grow if there is no performance based system in place. Then they gradually integrate merit-based system and allow high performers to have fast track career path.
- Standardize Processes and Parts: To achieve economy of scale, Samsung standardize processes and parts and majority of components are produced in Korea. This also enables them to manage product quality more effectively due to ease of control.
- Establish Risk Management System: They realize that risks are the fact of life. So they implement very comprehensive risk management system and their risk mitigation strategies are low inventory level, flexible capacity and redundant suppliers.
Conclusion
The secret sauce behind Samsung’s supply chain success is definitely “Best Practice Analysis”. They study how other world’s leading companies manage business and choose to adapt these best practices gradually.
Editors Note: Original article posted on SupplyChainOpz

Visit Supply Chain 24/7’s “Risk Management” Channel
Related: How Apple Has the Power to Make or Break a Supply Chain Supplier

Article topics
Email Sign Up