Editors’ Picks





Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 0.61
…of the Women in Supply Chain Initiative at the MIT Center for Transportation and Logistics. Date will discuss the importance of diversity in the supply chain and what she has learned talking to leaders of some of the largest supply chains in the world. Joining her onstage will be Alicemarie Geoffrion, who is president of packaging at DHL Supply Chain. She was recently named one of the Top 100 Women in Supply Chain by Supply Chain Digital. Geoffrion is also a member of the World Economic Forum. “We are thrilled to host two brilliant supply chain minds at our second…

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 0.61
…chains. The shift, according to a published report from MIT Economist David Autor, will affect both the engineers that design them, and companies that rely on them. “There's never been a better time to be a worker with special skills or the right education, because these people can use technology to create and capture value,” says Autor. “However, there's never been a worse time to be a worker with only 'ordinary' skills and abilities to offer, because computers, robots, and other digital technologies are acquiring these skills and abilities at an extraordinary rate.” One proposed solution to offset the growth…

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 0.60
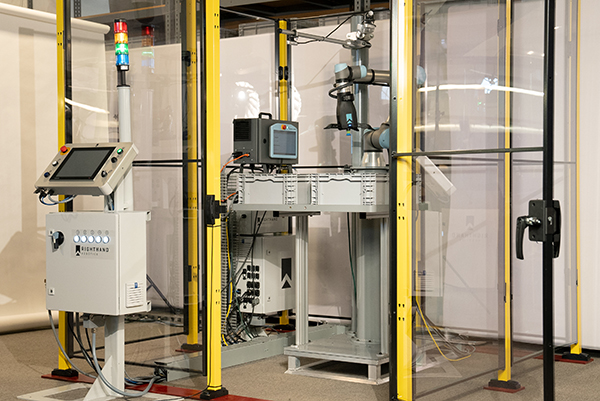
…the Harvard Biorobotics Lab, the Yale GRAB Lab, and MIT founded RightHand Robotics in 2015 to apply computer vision and machine learning to real-world grasping problems. The company said its data-driven, intelligent picking platform provides flexible and scalable automation for predictable order fulfillment. RightHand said RightPick 3, its latest robotic piece-picking system, “enables retailers to rise up to the new realities of online commerce.” RightPick 3 has a modular, industrialized hardware design and well-defined software application programming interfaces (APIs), said the company. It is designed to be integrator-friendly and complies with international standards, RightHand said. The company claimed that RightPick…

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 0.58
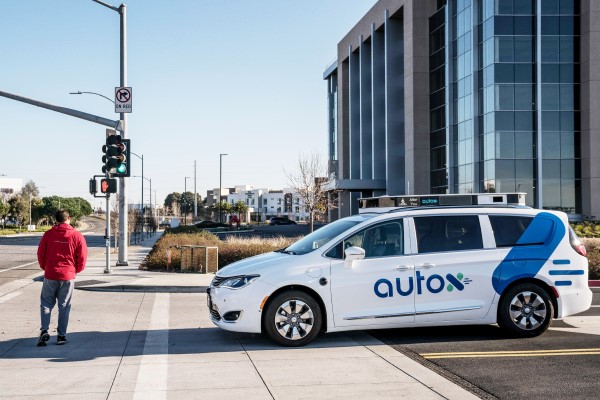
…Artificial Intelligence Laboratory at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT CSAIL). In addition, Xiao was an assistant professor at Princeton University and the founding director of the Princeton Computer Vision and Robotics Labs from 2013 to 2016. Shenzhen pioneers RoboTaxi testing in China AutoX's fully driverless RoboTaxi service has been “well received” by Shenzhen residents and officials alike, according to Ms. Wang, a representative of the company's operations team. Within the first 100 days of operation, AutoX RoboTaxi has won loyal users from the traditional ride-hailing market, she said. AutoX is the second permit holder for California Department of Motor…

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 0.57
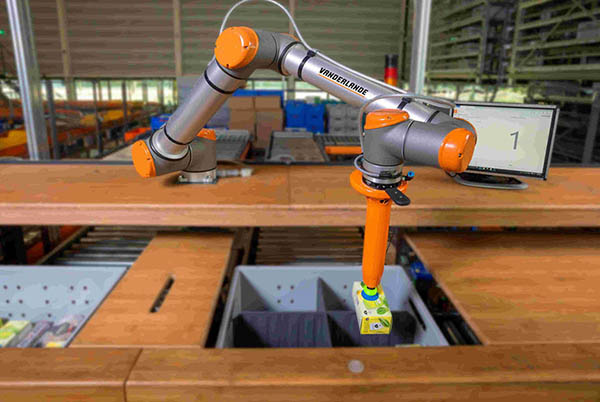
…the Harvard Biorobotics Lab, the Yale GRAB Lab, and MIT founded RightHand Robotics in 2015. Their stated goal was to apply grasping intelligence powered by computer vision and applied machine learning to real-world problems. The Somerville, Mass.-based company said its data-driven picking platform provides flexible and scalable automation for predictable order fulfillment. It raised $66 million in Series E funding last month. RightHand said it will be at the following events: MODEX 2022: The RightHand Robotics team is at Booth B8622, and the Vanderlande team is at at Booth B5406 from March 28 to 31 in Atlanta. LogiMAT 2022: RightHand…

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 0.57
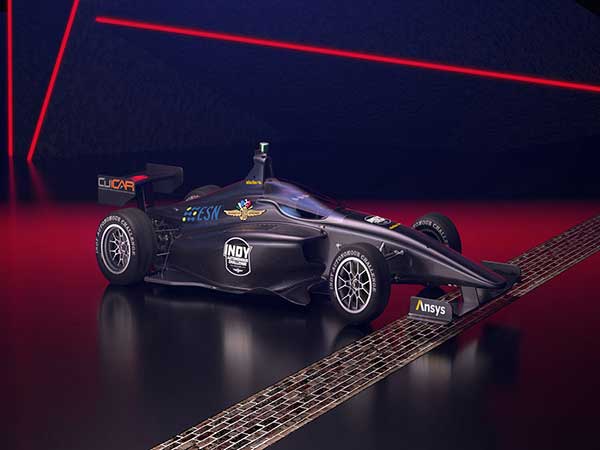
…racing,” says Charles Vorbach, controls systems architect for the MIT Driverless team. “Our team is excited to develop our entry using Ansys' simulation tools. We admire their use of sophisticated vehicle models, compatibility with open source systems like ROS2, and user-friendly code-generation that is intuitive enough for even non-software engineers. Most of all, Ansys' software reduces the amount of physical testing required, which will help safely speed development, especially in the world of COVID-19.” Ansys simulation solutions provide OEMs, automotive suppliers and mobility companies robust workflows for the design and validation of automated driving systems and components, including safety analysis,…
Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 0.57
…will encounter them.” A Moral Compass for Self-Driving Cars MIT researchers recently launched an online experiment, designed to explore the moral dilemmas faced by autonomous vehicles. Dubbed The Moral Machine (moralmachine.mit.edu), the online system is described as “a platform for gathering human perspective on moral decisions made by AI.” By MIT’s own count, it has collected 40 million decisions in 10 languages from millions of people in 233 countries and territories. Researchers published the first set of findings in a paper titled “The Moral Machine experiment,” Nature: International Journal of Science, October 2018. It includes charts explaining participants’ choices, such…

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 0.57
…from that.” Founders bring industry experience Saad is an MIT alumnus and co-founder of MassRobotics, an organization that supports more than 60 resident startups at its shared workspace in Boston. He previously led MassRobotics' partnership program, building relationships with more than 40 corporations. Saad has worked with entrepreneurs, researchers, and technologists from around the world. He also brings business management and development experience from multinationals Siemens and Nokia. Saad told Robotics 24/7 that he will be leaving MassRobotics after a transition period. “We are excited that Fady will remain involved in the robotics ecosystem and that his new efforts will…

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 0.55
…operators worldwide.” Harvard Biorobotics Lab, Yale GRAB Lab, and MIT researchers Tenzer, Leif Jentoft, and Lael Odhner founded RightHand Robotics in 2015 after winning a Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) manipulation challenge. They focused on solving the “holy grail” of warehouse automation—piece picking for supply chain and e-commerce fulfillment, said the Somerville, Mass.-based company. RightPick deals with complex picking RightHand Robotics launched its autonomous piece-picking product in 2017. The modular, data-driven RightPick platform uses artificial intelligence, edge computing, machine vision, grippers, and collaborative robot arms. Its workflows can quickly adapt to new SKUs for streamlined and scalable order fulfillment…
Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 0.55
…the term, it was coined by Charles Fine, an MIT professor, to define rapidly evolving industries – those with a fast clock speed that he likened to fruit flies that are born, mature and expire in a very short time. He argued that “in business today, all advantage is temporary. In order to survive-let alone thrive-companies must be able to anticipate and adapt to change, or face rapid, brutal extinction.“ Based on my week at Promat in Chicago, I’d argue that the clockspeed of our industry has been accelerating in an unprecedented fashion over the last three to five years.…

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 0.54
…received his Ph.D. in computer science in 2014 from MIT, where he developed and applied new theoretical tools for processing 3D orientation information to applications in computer vision and robot manipulation. Jared Glover, CEO of CapSen Robotics. Source: ARM Institute Prior to that, Glover completed his B.S. in computer science from Carnegie Mellon University, where he led a team developing robotic walkers. He has 20 years of research experience in robotics and computer vision and more than 500 paper citations. Glover is also on the boards of the Pittsburgh Robotics Network and the Catalyst Connection, a private non-profit that provides…

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 0.54
…now the Low-Power Computer Vision Challenge), outperforming teams from MIT, Qualcomm, Amazon, and others. ENOT has raised unspecified seed funding from New Nordic Venture. ENOT intends to cut computing costs ENOT.ai said its framework takes a trained neural network as input, after which it selects the sub-network with the lowest latency to ensure no accuracy degradation. The company said its neural architecture selection technology can achieve optimization ratios resulting in acceleration up to 20x and compression up to 25x. This can outperform other methods and reduce total hardware computing resource costs by as much as 70%, it claimed. ENOT explained…



